- | 10:56 am
The fascinating history of shopping and its influence on how we buy stuff today

It’s a sunny, spring Saturday morning in early 2019, and I’m having coffee in Brentwood, England, a small Essex town where I’ve never been before. I have a couple of hours to spare, so I’m planning to wander around and have a look in the shops. Then my phone pings: “Surprise!” It’s a promotion from M&S. “Here’s 20% off when you shop online.”
The Brentwood branch of M&S is just a couple of doors down from where I am. But the notification isn’t suggesting I go there. On the contrary, this special offer will deter me from shopping in an actual shop, on an actual high street, where I know I’d now be paying 25% more than if I bought online. It is, in effect, a counter-advertisement—taking me away from the shops and toward a virtual, online-only future.
Around this time, M&S had been closing stores in numerous locations. Many of these shops had been there for as long as people could remember, and were part of the towns’ identity. Like “our” NHS, and unlike most other commercial brands, M&S evokes a feeling of belonging to a shared history.
Looking back, my little counter-epiphany now seems to encapsulate something of the fraught shopping mood of three years ago. The incident felt like a painful sign of the contradictory state of British retail—and especially that part of it that is commonly known as the high street.
FROM STREET PEDDLERS TO SUPERMARKETS
Online shopping seemed to be the next and natural step along the path that began with the introduction of self-service. I started charting these developments more than 20 years ago when I wrote, Carried Away: The Invention of Modern Shopping. And a year after the sad Brentwood episode, at the start of 2020, I was coming to the end of writing my new book, Back to the Shops: The High Street in History and the Future. This investigates the different stages of shopping, from its early beginnings to the present.
This history stretches back to peddlers and weekly markets and runs through small fixed shops in towns and villages to the grand “destination” city department stores of the last part of the 19th century. Then, in the later 20th century, came self-service, to be followed in recent years by the move online.
Take fast fashion, for instance. We think of fast fashion as inseparable from a contemporary culture of rapid turnover. But a version of it can be found as far back as the 18th century, well before garments were mass-produced in factories. Clothes at this time were all sewn by hand.
In late 18th century London, a new type of shop appeared where, for a price, a lady or gentleman could commission a customized outfit that would be made up for them overnight. It offered an instant transformation into the style and class of the best social circles. But unlike modern fast fashion, it wasn’t cheap, and the clothes weren’t flimsy or soon discarded.
Mail-order shopping also has a rich history that seems to anticipate later developments. Catalogue companies, like Freeman’s or Kay’s, were massively popular in the middle of the 20th century. But despite its popularity, “the book” (the affectionate name for the big, “full color” catalogue) never posed a threat to the shops. Nevertheless, mail order was a form of virtual shopping at a distance, and now looks like a striking precursor to online shopping.
Perhaps the most surprising example of an early retail development whose beginnings have now disappeared from view, is the chain store. We tend to think of chain stores as having pushed independent shops out of the way in the late 20th century, with the result that every shopping mall and every High Street (if it survives at all) looks like all the rest. But, in fact, chain stores were everywhere a century earlier, including some of the names that are still well-known today.
WHSmith, the newsagent and bookseller, developed from the late 1840s alongside the growing railway network. There was soon a stall to be seen inside every station of any size, providing the passenger with novels or newspapers for their journey. In 1900, there were no fewer than 800 branches nationwide. From the beginning of the 20th century, Smith’s also had outlets on town shopping streets.
Boots the chemist was another 19th century chain that is still a standard High Street presence. The first Boots shop opened in Nottingham in 1849. By the turn of the century, there were around 250 branches—and 1,000 by the early 1930s.
THE SELF-SERVICE REVOLUTION
If online retail was the new feature of early 21st century shopping, self-service was the shopping revolution of the 20th century.
Self-service reached Europe after the Second World War. In the U.S., it had been an accidental invention of the Great Depression, when abandoned factories and warehouses were turned into makeshift, cut-price outlets. Customers picked out goods as they walked around and paid for everything at the end. By the 1940s, this new type of store was well established, often in regional chains, as the “super market.” Postwar, this new American mode of retail operation was exported to the rest of the world.

[Photo: Sainsbury Archive]
Promoted as a modern, efficient way to shop, self-service entailed both a different type of store layout and new norms of customer and shop-worker behavior. Before this, every purchase was asked for over the counter, item by item, and the assistant “served” the customer personally. Few goods were packaged, so every order was literally customized: measured or weighed and then wrapped.
But self-service did away with all this. There was no need for counter service if customers were making their own selections. All available goods were put out on display, within reach. No need to ask someone to fetch them. And there was no one else waiting behind you for their turn to be served. You could take your time, look around, or get it done at speed. It was your choice.
This was a newly impersonal shopping environment. The customer was in control of the pace and the selection, but they were on their own and there was no longer someone standing there to serve them. For shop workers, meanwhile, the abolition of counter service meant that their various skills, including their people skills, were made redundant. So too was their often detailed knowledge of the products they sold.
When the customer did encounter a person across a counter, it was not to ask for advice about what to buy; it was simply to pay and get out. Nor was the checkout for chatting. Like factory workers, cashiers had to keep up to speed.
The whole process was meant to be more efficient, a saving of time and money for businesses and customers alike. The customer, notably, was seen now as someone for whom time was a finite and valuable resource. In this way, the shift to self-service perfectly matched with some large social changes of the postwar decades.
As late as the 1960s, for example, “housewife” was the default designation for women over the age of 16 (even though many had part- or full-time jobs). But the “housewife” would soon be replaced by the double-shift working woman, eternally “juggling” the demands of both home and work. By the end of the 20th century, now with the help of a fridge and a car, the daily walk to the local shops had been replaced by a weekly trip to the supermarket, where everything was available under one roof, and the shopping was now a substantial task.

[Photo: Sainsbury Archive]
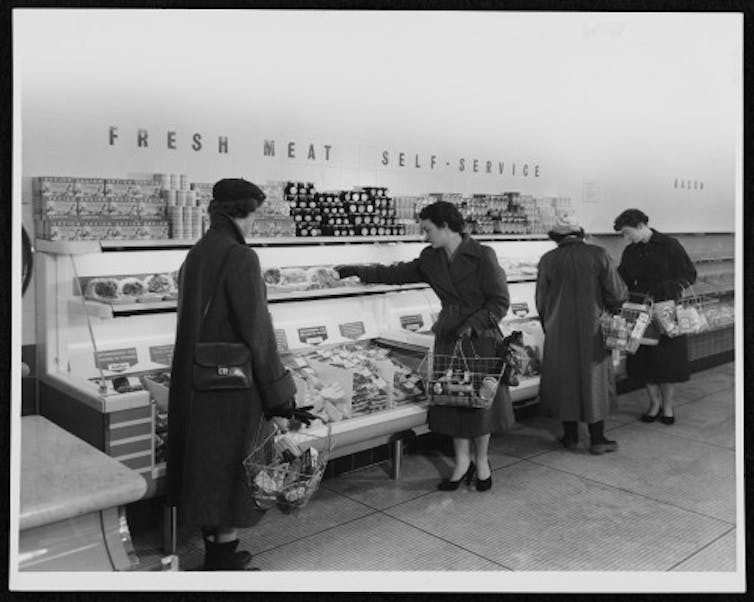
The first 1950s self-service stores are distant enough today to have become the subject of mild nostalgia, obscuring the original picture of smart efficiency. Black-and-white photos from the archives show people (particularly women) of every social type gamely learning to manage the curious “basket” containers provided for them to carry around on their arms and fill up as they walked around the shop. What looks odd now, many decades later, is how little they’re buying—just a few jars and tins.

[Photo: Sainsbury Archive]
SAVE TIME ONLINE
With self-service firmly established to assist supposedly “time-poor” consumers, the stage was set for internet shopping to promise an even more efficient way of doing things.
An Ocado flyer from early 2019 displays the caption: “More time living, less time shopping,” as if living and shopping have become mutually exclusive. And crucially, it is not money but time that is the quantifiable currency of the promotion.
In this way, the online upgrade appears to remove all remaining real-life interference from the task of shopping. You don’t have to take yourself anywhere to get to the store, which never closes. There are no empty shelves; everything is always there on the screen. There is still a trolley or basket, but not one that you have to push or carry, and it will hold whatever you “add” to it, irrespective of volume or quantity.
The shop assistant is wholly absent from the screen, although there are downgraded virtual versions available in the form of programmed chat-bots. With online shopping, the backstage work that “fulfills” an order occurs in a storage facility far away and is invisible to the customer. But in large self-service settings, like supermarkets and DIY mega-stores, the role of the checkout cashier had already been reduced to that single scanning function, requiring no specialist range of skills and no particular knowledge of any one of the thousands of possible things, from bananas to baby wipes, that they might be rapidly moving along.
BACK TO THE “REAL” SHOPS?
Town centers had been dying a much discussed death for years, as more and more shops were being closed down and stayed unused.
But amid the doom and gloom, some towns were taking action to resist the trend, battling back with collective imagination and sometimes with significant financial backing. Shrewsbury Town Council revitalized a 1970s market building to make it a thriving center for food stalls, cafés, and specialist shops. The council also bought a couple of rundown indoor shopping centers in the town, which can now be redeveloped with community interests in mind.
On a smaller scale is Treorchy in South Wales, which won a national best High Street prize in 2019, thanks to its flourishing independent shops and cafés. They all worked together to organize cultural events with the help of an enterprising chamber of commerce.
Still, initiatives like these were the exception. For the places at the other extreme, where boarded-up units were everywhere, the call to keep shops open could sound like a hopeless plea, and too late to make a difference.
LOCKDOWN’S IMPACT
In the first weeks of lockdown, it seemed that the pandemic would hasten the move online, by closing down most of the shops that were left and seemingly leaving online as the only option. But as that slow, strange time went on, it became clear that something quite different was going on. Two years later, we can see that the lockdowns brought about a return to slower, more local, and personal modes of shopping.
The shops still open for normal business—those that officially qualified as providers of “essential” goods—were being used in new (and yet old) ways. They became places to go for some vital variation in our daily routines.
People also began to make a point of supporting and using independent local shops. At the same time, home deliveries were being organized by these smaller shops, often working together in groups. This was the case with Heathfield, a few miles from Thomas Turner’s village in East Sussex. And it had nothing to do with the networks set up by the supermarkets and other big chains.
In the media, shop assistants, working on checkouts or filling shelves, began to be referred to as “frontline workers.” The implication of this “promotion” was that they were doing invaluable work that was comparable to the public-spirited dedication of NHS employees.
The local high street seemed to be benefitting from renewed appreciation. It was as if the pandemic had demonstrated what shops were really for, and why we should not let them go. To say that shops—real shops—are a much-needed community resource used to sound worthy and well-meaning. Now it just states the obvious.
A RETURN TO HOME DELIVERY
Meanwhile, another related revival is happening: home delivery. This is often assumed to have been an online invention, promoted by big supermarkets as the latest expansion of their networks and by big stores of all kinds.
But until the middle of the 20th century, most shops offered home delivery as a matter of course. For many food products, like milk or meat, this arrangement was the default. The butcher’s boy brought round the tray of meat, and the milkman delivered the bottles direct to your doorstep every morning.
With self-service came the end of most home delivery services, too. When bigger supermarkets were built on the edges of towns, in the 1980s and 1990s, the basket became a big trolley, and people put all the bags they came out with into their car. As with all the other changes associated with “self”-service, the difference was that customers were doing this work themselves.
The new delivery services offered by smaller, independent stores that started up during lockdown represented a return to local arrangements that were standard before the arrival of self-service. Yet, orders are often now made online. In this case, then, new technology has actively contributed to the revival of an older form of shopping.
In the East Sussex village of Rushlake Green, for example, the local shop began to offer home deliveries. This was so successful that they acquired a new delivery van with their name on the side. This marked something of a return to the 1930s, when local shops first started investing in a “motor van” to make deliveries (a new trend much remarked on in the trade handbooks of the time).
As it happens, this joining of the traditional with the latest tech is itself a long established phenomenon in the history of retail distribution. New modes of transport and communication have repeatedly modified the existing conditions of shopping, and the current manifestation has striking antecedents.
Virginia Woolf’s last novel, Between the Acts, offers a nice illustration of this. It is set at the end of the 1930s, when the installation of domestic telephones was beginning to make it possible for affluent customers to ring up the shop and order their meat or groceries for delivery without having to leave the house or send a servant.
One scene in the novel has a country lady distractedly ordering fish “in time for lunch” while she brushes her hair in front of the mirror and murmurs lines of poetry to herself. A few pages later, just as she requested, “The fish had been delivered. Mitchell’s boy, holding them in a crook of his arm, jumped off his motorbike.”
In Woolf’s time, this mode of transport, along with the phoned-in order, was a notable innovation, allowing just-in-time gourmet food deliveries. Almost a century later, the exclusive telephone is now the semi-universal smartphone, but the method of ordering at a distance is the same. And as it turns out, the motorbike has not been superseded in the online age of Deliveroo.