- | 8:00 am
These smart contacts will monitor your eyes 24/7 for glaucoma
The disease can steal a person’s vision without early warning signs or pain and affects more than 80 million people worldwide.
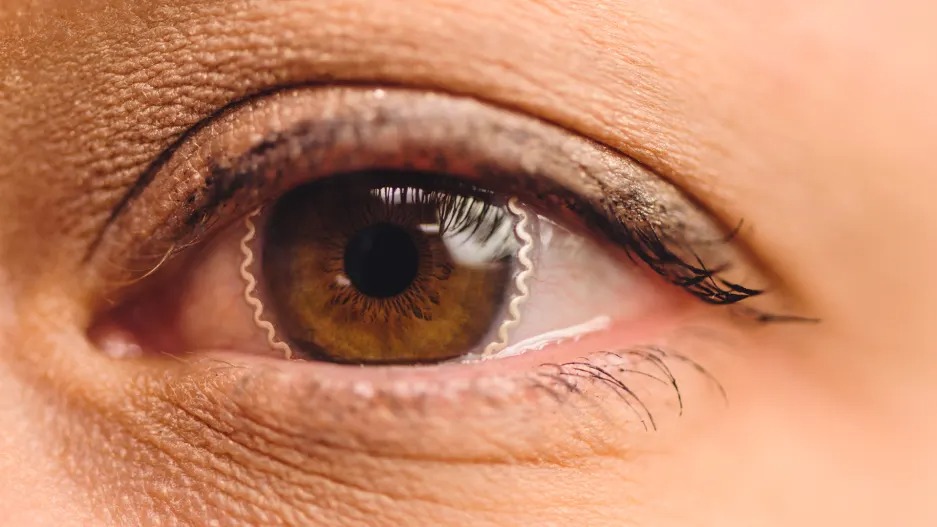
The researchers developed the new ocular technology to monitor patients’ intraocular pressure (IOP) readings more comfortably and accurately.
The tech serves as another option for eye specialists to identify glaucoma. The disease can steal a person’s vision without early warning signs or pain and affects more than 80 million people worldwide, according to the Glaucoma Research Foundation.
The only known modifiable risk factor is lowering a person’s IOP, which is difficult to monitor for long periods of time, particularly during sleep.
While exams can be performed in a specialist’s office, and at-home monitoring systems are available, these all have their limitations. For instance, in-office measures are time consuming, and current at-home technology is difficult to use, uncomfortable, and doesn’t gather sufficient data at the right time periods or over long enough time periods for specialists to appropriately use the information to make optimized treatment decisions.
As reported in the journal Nature Communications, the new technology can gather important IOP measurements for 24-hour cycles, even during sleep.
“The largest increase in IOP often occurs while people are lying down, when overnight IOP is typically 10% to 20% greater than daytime IOP. Vision loss may occur during sleep without the patient noticing it, even if daytime in-clinic or at-home measurements indicate normal IOP,” says Chi Hwan Lee, associate professor of biomedical engineering in Purdue University’s Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering who has a joint appointment in the School of Mechanical Engineering and a courtesy appointment in the School of Materials Engineering.

Lee, who has worked on this technology for six years, specializes in sticktronics, which are sticker-like items that contain electronics or smart technology. His lab develops wearable biomedical devices that can continuously monitor chronic diseases or health conditions in an unobtrusive manner.
Some of the current wearable tonometers (devices that measure the pressure inside one’s eyes) are equipped with an integrated circuit chip, which contributes to increased thickness and is stiffer than a typical commercial soft contact lens, in many cases causing discomfort for patients. Lee’s version is different.
“To address this unmet need, we developed a unique class of smart soft contact lenses built upon various commercial brands of soft contact lenses for continuous 24-hour IOP monitoring, even during sleep at home,” Lee says. “Our smart soft contact lenses retain the intrinsic lens features of lens power, biocompatibility, softness, transparency, wettability, oxygen transmissibility, and overnight wearability. Having all these features at the same time is crucial to the success of translating the smart soft contact lenses into glaucoma care, but these features are lacking in current wearable ocular tonometers.”
The tonometer on the new contact lens sensor creates a wireless recording that is transmitted to a receiver in a pair of eyeglasses for daytime IOP measurement and a sleep mask for IOP measurement when sleeping.
The complete 24-hour IOP rhythm data can be shared with clinicians remotely via an encrypted server. The tonometer can generate an audible alert for detection of IOP elevation, allowing appropriate action to take place and reducing the need for clinic visits.
“This tonometer is significantly more comfortable than any other type of contact lens sensor we have come across and more comfortable than any currently available commercially available IOP sensor,” says Pete Kollbaum, associate dean for research and director of the Borish Center for Ophthalmic Research at the Indiana University School of Optometry.
“This is related to the technology that Lee uses to apply the sensor to the lens, retaining a very thin overall sensor, and to the fact that the lens itself is a time-tested, commercially available lens, leveraging the clinical studies and associated time and money the contact lens manufacturers have spent to assure a comfortable lens.”
Not only do the specialized contact lenses provide crisp vision, just as any contact lens would, but the technology also expands the benefits for both patients and eye specialists, who have wanted less expensive and more comfortable ways to monitor eye changes for years, Kollbaum says.
“The eye is a very challenging body part that is even softer, more sensitive, and curvilinear when compared to the skin,” Lee says. “We hope our approach can be also tailored for aiding and detecting other chronic ocular diseases and for other functions.”
Lee and colleagues have a proposal for additional clinical trials with glaucoma patients who have dry eye diseases or who have had glaucoma surgery. They are also working with Boomerang Ventures, with which Purdue has a partnership, to incorporate the technology into clinical practice.
Additional coauthors are from Johns Hopkins University, Indiana University, and Purdue University. The technology was disclosed to the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization (OTC), which has applied for a provisional patent from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office to protect the intellectual property.
This article was originally published on Futurity.org (sourced from Purdue University News) and is reprinted with permission.