- | 8:00 am
From ‘Her’ to ChatGPT, here’s how sci-fi and tech feed off each other
The dynamic between Hollywood and Silicon Valley is a “sci-fi feedback loop.”
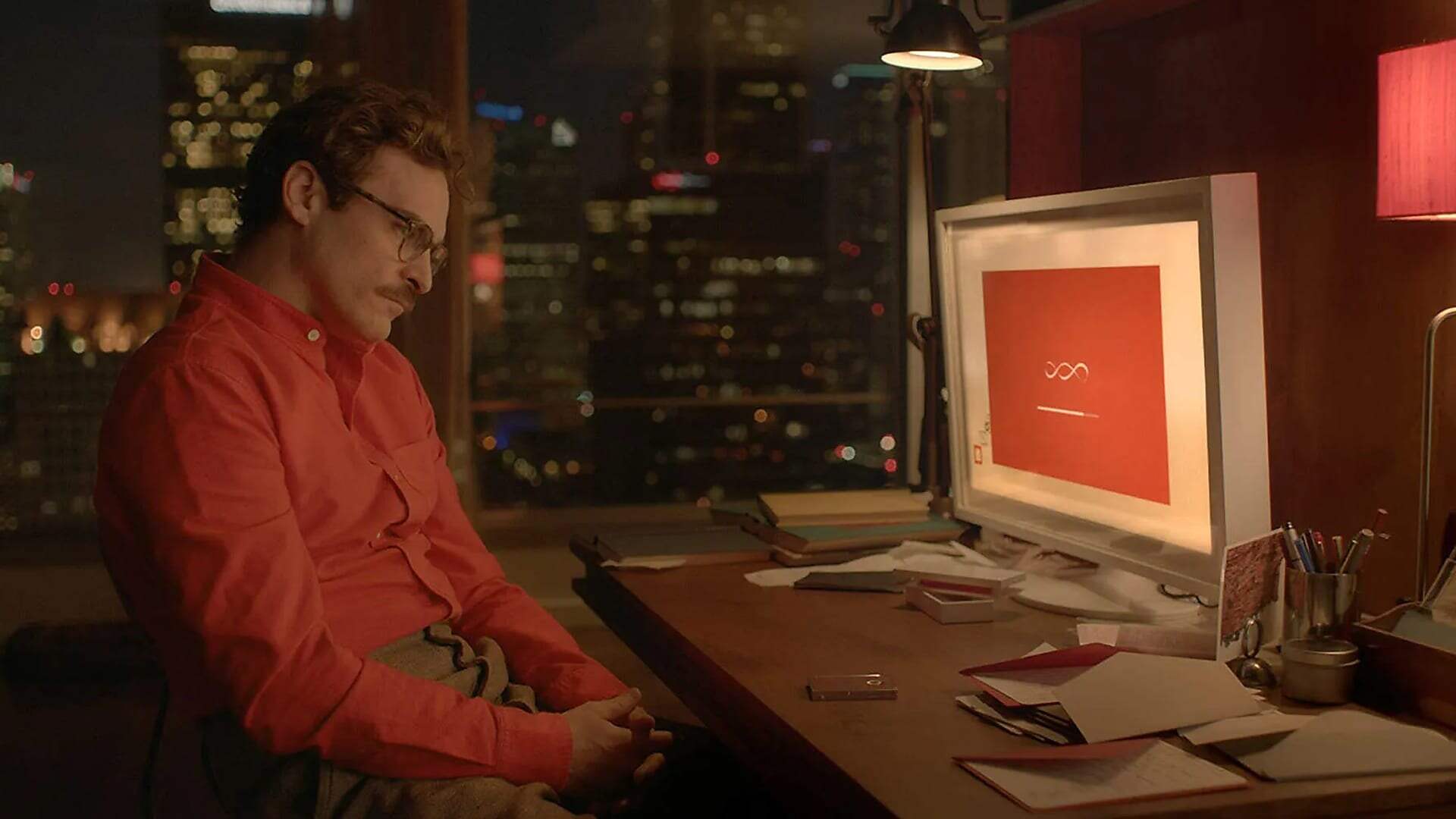

In May 2024, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman sparked a firestorm by referencing the 2013 movie “Her” to highlight the novelty of the latest iteration of ChatGPT.
Within days, actor Scarlett Johansson, who played the voice of Samantha, the AI girlfriend of the protagonist in the movie “Her,” accused the company of improperly using her voice after she had spurned their offer to make her the voice of ChatGPT’s new virtual assistant. Johansson ended up suing OpenAI and has been invited to testify before Congress.
This tiff highlights a broader interchange between Hollywood and Silicon Valley that’s called the “sci-fi feedback loop.” The subject of my doctoral research, the sci-fi feedback loop explores how science fiction and technological innovation feed off each other. This dynamic is bidirectional and can sometimes play out over many decades, resulting in an ongoing loop.
FICTION SPARKS DREAMS OF MOON TRAVEL
One of the most famous examples of this loop is Moon travel.
Jules Verne’s 1865 novel “From the Earth to the Moon” and the fiction of H.G. Wells inspired one of the first films to visualize such a journey, 1902’s “A Trip to the Moon.”
The fiction of Verne and Wells also influenced future rocket scientists such as Robert Goddard, Hermann Oberth and Oberth’s better-known protégé, Wernher von Braun. The innovations of these men—including the V-2 rocket built by von Braun during World War II—inspired works of science fiction, such as the 1950 film “Destination Moon,” which included a rocket that looked just like the V-2.
Films like “Destination Moon” would then go on to bolster public support for lavish government spending on the space program.
CREATIVE SYMBIOSIS
The sci-fi feedback loop generally follows the same cycle.
First, the technological climate of a given era will shape that period’s science fiction. For example, the personal computing revolution of the 1970s and 1980s directly inspired the works of cyberpunk writers Neal Stephenson and William Gibson.
Then the sci-fi that emerges will go on to inspire real-world technological innovation. In his 1992 classic “Snow Crash,” Stephenson coined the term “metaverse” to describe a 3-D, video game-like world accessed through virtual reality goggles.
Silicon Valley entrepreneurs and innovators have been trying to build a version of this metaverse ever since. The virtual world of the video game Second Life, released in 2003, took a stab at this: Players lived in virtual homes, went to virtual dance clubs and virtual concerts with virtual girlfriends and boyfriends, and were even paid virtual dollars for showing up at virtual jobs.
This technology seeded yet more fiction; in my research, I discovered that sci-fi novelist Ernest Cline had spent a lot of time playing Second Life, and it inspired the metaverse of his bestselling novel “Ready Player One.”
The cycle continued: Employees of Oculus VR—now known as Meta Reality Labs—were given copies of “Ready Player One” to read as they developed the company’s virtual reality headsets. When Facebook changed its name to Meta in 2021, it did so in the hopes of being at the forefront of building the metaverse, though the company’s grand ambitions have tempered somewhat.
Another sci-fi franchise that has its fingerprints all over this loop is “Star Trek,” which first aired in 1966, right in the middle of the space race.
Steve Perlman, the inventor of Apple’s QuickTime media format and player, said he was inspired by an episode of “Star Trek: The Next Generation,” in which Lt. Commander Data, an android, sifts through multiple streams of audio and video files. And Rob Haitani, the designer of the Palm Pilot’s operating system, has said that the bridge on the Enterprise influenced its interface.
In my research, I also discovered that the show’s Holodeck—a room that could simulate any environment—influenced both the name and the development of Microsoft’s HoloLens augmented reality glasses.
FROM ALICE TO ‘HER’
Which brings us back to OpenAI and “Her.”
In the movie, the protagonist, Theodore, played by Joaquin Phoenix, acquires an AI assistant, “Samantha,” voiced by Johansson. He begins to develop feelings for Samantha—so much so that he starts to consider her his girlfriend.
ChatGPT-4o, the latest version of the generative AI software, seems to be able to cultivate a similar relationship between user and machine. Not only can ChatGPT-4o speak to you and “understand” you, but it can also do so sympathetically, as a romantic partner would.
There’s little doubt that the depiction of AI in “Her” influenced OpenAI’s developers. In addition to Altman’s tweet, the company’s promotional videos for ChatGPT-4o feature a chatbot speaking with a job candidate before his interview, propping him up and encouraging him—as, well, an AI girlfriend would. The AI featured in the clips, Ars Technica observed, was “disarmingly lifelike,” and willing “to laugh at your jokes and your dumb hat.”
But you might be surprised to learn that a previous generation of chatbots inspired Spike Jonze, the director and screenwriter of “Her,” to write the screenplay in the first place. Nearly a decade before the film’s release, Jonze had interacted with a version of the ALICE chatbot, which was one of the first chatbots to have a defined personality—in ALICE’s case, that of a young woman.
The ALICE chatbot won the Loebner Prize three times, which was awarded annually until 2019 to the AI software that came closest to passing the Turing Test, long seen as a threshold for determining whether artificial intelligence has become indistinguishable from human intelligence.
The sci-fi feedback loop has no expiration date. AI’s ability to form relationships with humans is a theme that continues to be explored in fiction and real life.
A few years after “Her,” “Blade Runner 2049” featured a virtual girlfriend, Joi, with a holographic body. Well before the latest drama with OpenAI, companies had started developing and pitching virtual girlfriends, a process that will no doubt continue. As science fiction writer and social media critic Cory Doctorow wrote in 2017, “Science fiction does something better than predict the future: It influences it.”
Rizwan Virk is a faculty associate and PhD Candidate in Human and Social Dimensions of Science and Technology at Arizona State University.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.