- | 9:00 am
How this 3-person architecture firm designed the world’s largest museum
Heneghan Peng Architects didn’t have a building to their name. Then they won the chance to design the Grand Egyptian Museum, Cairo’s new $1 billion tourist attraction.

With more than 100,000 artifacts dating back thousands of years, nearly 900,000 square feet of floor space, a site that spans more than 120 acres, and a total price tag estimated to be more than $1 billion, it’s not hyperbole to call the Grand Egyptian Museum outside Cairo, Egypt, the most significant museum project in recent decades. It’s the kind of blockbuster building that would have even the starriest of starchitects salivating at the chance to lay claim to what’s likely become one of Egypt’s most visited tourist attractions.
So, in hindsight, it’s a bit unexpected that the architecture firm that won the museum’s international design competition way back in 2002 was a little-known office from Ireland with no completed projects to its name and only three people on staff.
![[Photo: Iwan Baan]](https://images.fastcompany.com/image/upload/f_webp,q_auto,c_fit,w_1024/wp-cms-2/2025/10/13-91432907-egyptian-museum-redesign.jpg)
[Photo: Iwan Baan]
Dublin-based Heneghan Peng Architects was virtually unknown when its concept was chosen, unanimously, out of more than 1,500 submissions as the winning design. “We hadn’t built any buildings,” says Róisín Heneghan, the firm’s cofounder. “We had one project just starting on site when we won the competition.”
A lot has changed since then. The museum had an initial target opening date set for 2007, but several delays caused by the global financial crisis, the Arab Spring, and the COVID pandemic kept stretching the timeline. Heneghan Peng Architects’ design is now fully built and, as of November 1, open to the public.
![[Photo: courtesy Grand Egyptian Museum]](https://images.fastcompany.com/image/upload/f_webp,q_auto,c_fit,w_1024/wp-cms-2/2025/10/16-91432907-egyptian-museum-redesign.jpg)
[Photo: courtesy Grand Egyptian Museum]
Thousands of years of history
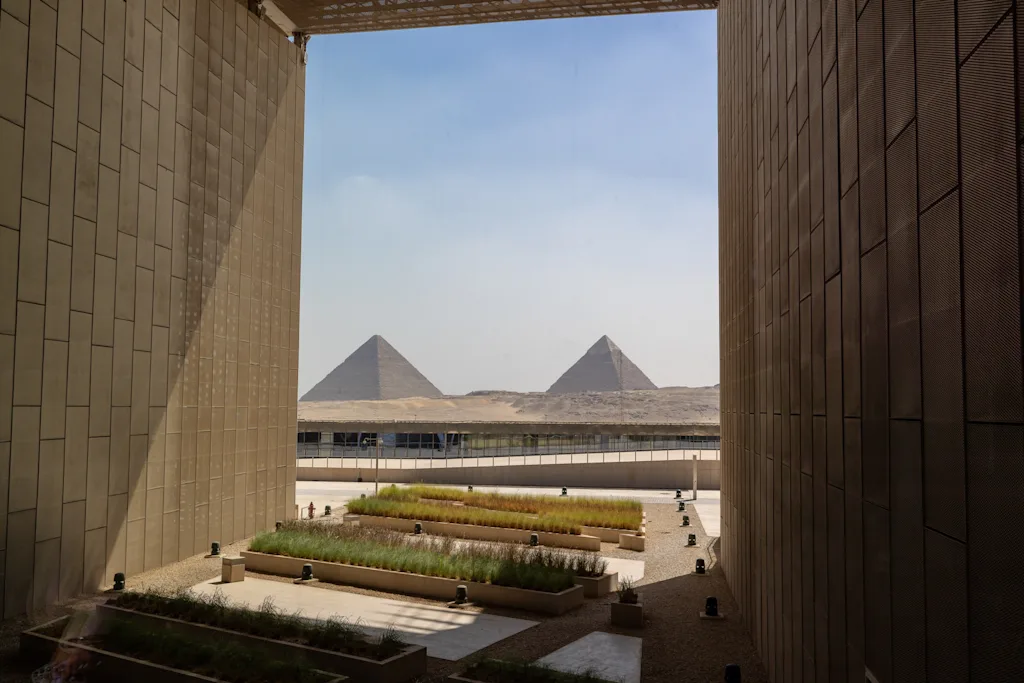
The Grand Egyptian Museum’s design is a sprawling spread of airplane hangar-sized concourses, sculpted landscapes, conservation workshops, and a network of underground storage facilities. The museum building itself is a cavernous space with 12 main galleries and direct views of the pyramids of Giza.
A vast entrance hall sits under a tall sawtooth roof that doubles as an open-air pavilion, shading a ticketing area accented by a 30-foot-tall statue of Ramses II that’s more than 3,000 years old. On the facade, throughout the landscape, and even within the building’s structure, pyramid shapes abound.
![[Photo: courtesy Grand Egyptian Museum]](https://images.fastcompany.com/image/upload/f_webp,q_auto,c_fit,w_1024/wp-cms-2/2025/10/14-91432907-egyptian-museum-redesign.jpg)
[Photo: courtesy Grand Egyptian Museum]
Central to the design, according to Heneghan, is not so much the main building but the placement of the museum itself. “People were saying to us, ugh, you Westerners, you all are so fascinated by the desert, but Egypt is about the Nile,” she says. That led the architects to think first about how the museum should fit into that dichotomy.
With a site selected near the famous pyramids in Giza, just on the fringe of Cairo’s urban footprint, it was clear that the museum would sit in the middle space between the desert and the Nile valley, a space that has been carved away by millennia of river flow. “There’s a 50-meter difference in level between one side of the site and the other, because that’s where the desert and the Nile met,” Heneghan says. “When you’re coming out of the city, you see the pyramids on the plateau. So what we decided was that the museum should never go above the plateau level, but that it should exist between the plateau and the Nile Valley.”
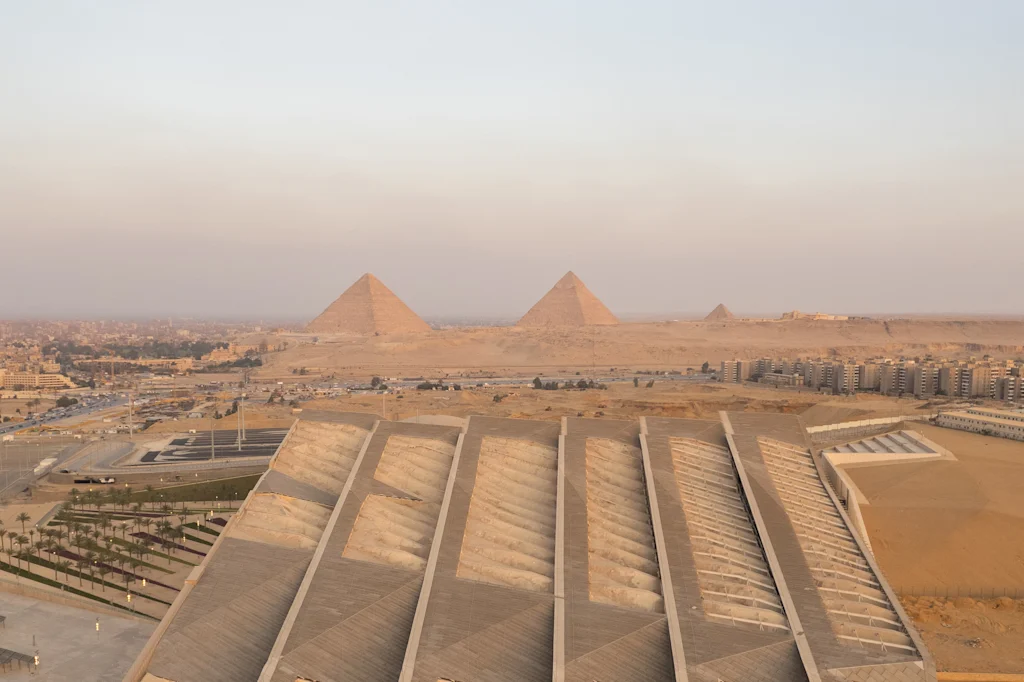

[Photo: Georges & Samuel Mohsen/The GS Studio/Heneghan Peng Architects
Despite grand ceilings capable of holding towering statues, the building sits low to the ground, with a fair amount of its bulk sunk into the landscape. The design of the Grand Egyptian Museum utilizes large walkways and views within the museum to give visitors a zoomed-out experience of the sprawling history represented in the galleries.
![[Photo: courtesy Grand Egyptian Museum]](https://images.fastcompany.com/image/upload/f_webp,q_auto,c_fit,w_1024/wp-cms-2/2025/10/09-91432907-egyptian-museum-redesign.jpg)
[Photo: courtesy Grand Egyptian Museum]
The first part of the museum visitors see after they enter is a long staircase bordered by thousands of artifacts, sarcophagi, and statuary that tracks the entire 4,000 year span of Egypt’s pharaonic history. It’s a walking crash course for the mostly international visitors to the museum before reaching the top where more discrete sections of Egypt’s ancient history are explored in more depth. Its main galleries cover themes like kings and queens, religious belief systems, and ancient Egyptian society, and the museum features an extensive collection of artifacts from the tomb of King Tutankhamun. The museum’s layout allows each of these galleries to stand on its own, but with visual connections to the others in order to tie them into a broader arc of history.
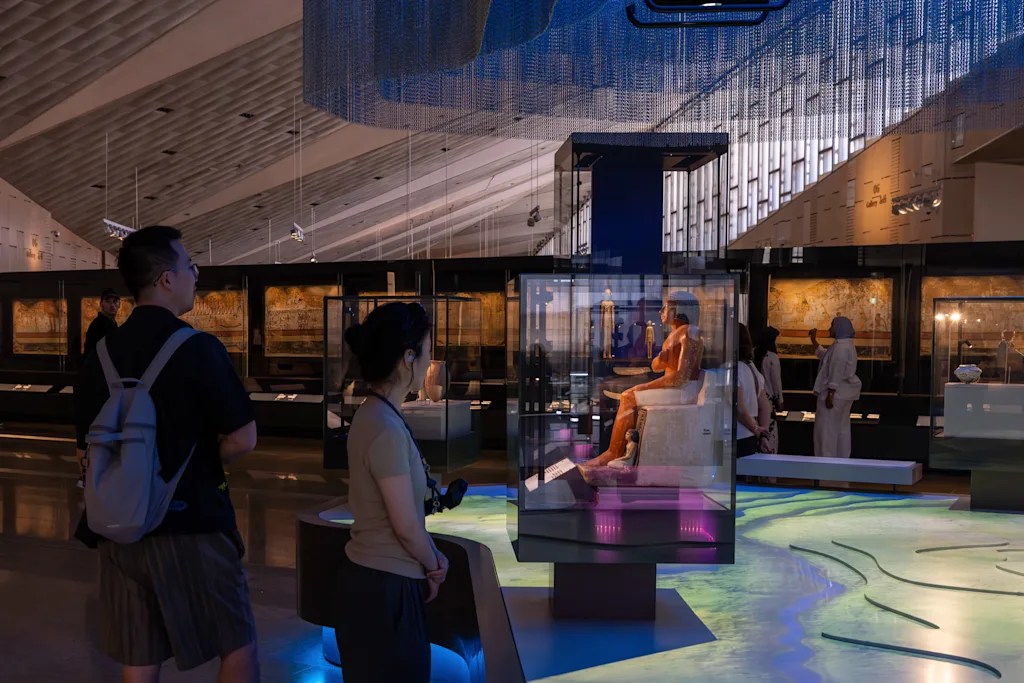

[Photo: Georges & Samuel Mohsen/The GS Studio/Heneghan Peng Architects
“The galleries are themed, but at the same time from different points you can see across, so you can make connections across the whole timescale,” Heneghan says. “That helped organize it. If we had tried to make it human-scaled, I think we would have found it more difficult.”
![[Photo: courtesy Grand Egyptian Museum]](https://images.fastcompany.com/image/upload/f_webp,q_auto,c_fit,w_1024/wp-cms-2/2025/10/08-91432907-egyptian-museum-redesign.jpg)
[Photo: courtesy Grand Egyptian Museum]
A engineering feat
The architects also had to grapple with the realities of designing such a massive structure in the desert heat of Egypt. Partly out of consideration for the operational costs of running such a space, they designed the galleries to pull in daylight from lateral angles that’s dappled through metal shading structures and overhangs. This approach also works with the collections on display. “It’s quite a lot of stone,” Heneghan says. “And stone works well with natural daylight.”
To handle the sheer weight of the statues on display, the building has incredibly thick concrete floors, which also serve to regulate the building’s climate, absorbing the cool night temperatures and slowly releasing it during the heat of the day. “What we were trying to do is make a really heavy structure, like a church,” Heneghan says.

[Photo: Georges & Samuel Mohsen/The GS Studio/Heneghan Peng Architects
Though Heneghan Peng Architects are the design architects of the Grand Egyptian Museum, they had plenty of help bringing the concept to fruition. Even at the competition stage, once they were named one of several finalists, they called in extra assistance from the engineering firms Arup and Buro Happold. Cairo-based Raafat Miller Consulting is credited alongside Heneghan Peng Architects as the project’s architect. Given the many delays that have hampered the project, Heneghan says her firm has essentially had very little to do with the design since it was largely finalized around 2009. “Once it went into construction, we weren’t really involved,” she says.
The project has evolved since then, with new structural, technological, and material changes that have necessarily altered the overall design. Heneghan says the facade of the building is a departure from a more reserved approach in the initial design, but she accepts that some tweaks were inevitable. “You know, 16 years is a really long time,” she says.
But there are also parts of the final museum that were among the architect’s initial thinking about what this museum could be, way back in 2002. Heneghan seems gratified that certain major elements like the grand staircase leading up to the main galleries and the direct views of the pyramids made it through after all these years. “Some things are very much what was envisaged,” she says.